If you have chronic hip pain that doesn’t improve with treatments like medication or physical therapy, hip replacement surgery might be a solution to help you live a more active and pain-free life. Hip replacement surgery is one of the most common and successful procedures offering significant relief to people with hip problems.
What is Hip Replacement Surgery?
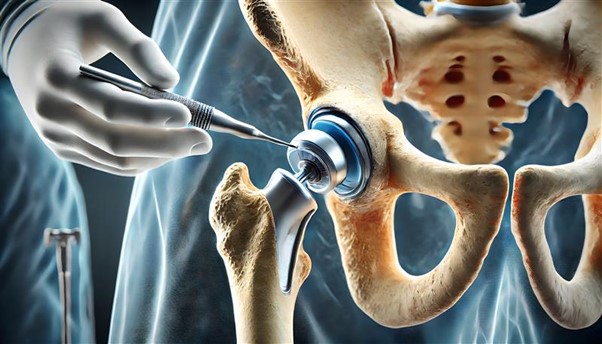
Hip replacement surgery is a procedure where a damaged or worn-out hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint. The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, where the ball is the top of the thigh bone (femur), and the socket is a part of the pelvis. Over time, due to injury, arthritis, or wear and tear, this joint can become damaged, causing pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving.
In hip replacement surgery, both the ball (femoral head) and the socket (acetabulum) are replaced with prosthetic parts made from materials like metal, ceramic, or plastic. The purpose of the surgery is to relieve pain, improve joint function, and restore your ability to perform everyday tasks.
When Do You Need Hip Replacement?
Your doctor may recommend hip replacement surgery if your hip pain is interfering with daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or getting out of a chair, and other treatments are no longer effective. Some common reasons people opt for hip replacement surgery include:
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most common reason for hip replacement. It happens when the cartilage in the hip joint breaks down over time, causing the bones to rub together, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and damage to the hip joint.
- Hip Fractures: A severe hip fracture that doesn’t heal properly or causes persistent pain may require hip replacement.
- Avascular Necrosis: In this condition, the blood supply to the hip bone is interrupted, causing the bone to die and the joint to collapse.
How is Hip Replacement Performed?
Hip replacement surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, which means you’ll be asleep during the procedure. It usually takes about 1 to 2 hours.
The surgeon begins by making an incision on the side or front of your hip to access the joint. They then remove the damaged ball and socket, replacing them with an artificial joint. The prosthetic parts are carefully fitted to ensure proper alignment and function. In some cases, a minimally invasive approach is used, which involves smaller incisions for a quicker recovery.
After the surgery, the incision is closed, and the joint is checked to ensure proper movement and stability. You’ll be monitored in the recovery room before being moved to a hospital room for further care.
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery
There are two main types of hip replacement surgery:
- Total Hip Replacement
In total hip replacement, both the ball (femoral head) and the socket (acetabulum) are replaced with artificial components. This procedure is most common and is typically recommended when the hip joint has significant damage.
- Hip Resurfacing
In hip resurfacing, the damaged areas of the femoral head and acetabulum are covered with a metal cap instead of removing the entire femoral head. This procedure is often used in younger patients with less joint damage, as it preserves more of the natural bone.
Benefits of Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery can offer several important benefits:
- Pain Relief: The most significant benefit is the relief from chronic hip pain, allowing you to return to daily activities without the constant discomfort.
- Improved Mobility: Many people experience better mobility after surgery, with a greater range of motion, improved ability to walk, and less stiffness.
- Better Quality of Life: After recovery, most people can return to their normal activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and exercising. This greatly improves overall quality of life.
- Long-Term Relief: Hip replacements are designed to last many years. With modern advancements, many artificial hips can last 15 to 20 years or more.
Risks and Possible Complications
While hip replacement surgery is generally safe, like any major surgery, it carries some risks. These include:
- Infection: Though rare, infections can occur at the incision site or in the joint itself. Surgeons take precautions to minimize this risk.
- Blood Clots: After surgery, there’s a risk of blood clots forming in the legs, which can travel to the lungs. Doctors may recommend exercises or devices to prevent this.
- Dislocation: In the first few months after surgery, the new joint may dislocate. Your doctor will provide instructions on how to avoid certain movements that could lead to dislocation.
- Implant Wear and Tear: Over time, the artificial joint may wear out or become loose, especially in younger or more active individuals. In some cases, a second surgery (revision) may be required.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: While rare, there’s a small risk that nerves or blood vessels near the hip could be injured during the surgery.
Recovery After Hip Replacement Surgery
Recovery from hip replacement surgery is a gradual process. The amount of time it takes to fully recover can vary depending on your overall health, age, and the type of surgery you had. Here’s what you can expect during the recovery process:
Immediately After Surgery (0-2 Weeks)
You’ll stay in the hospital for a few days after surgery. The healthcare team will help you with mobility, such as walking with a walker or crutches, and teach you how to safely get in and out of bed. Pain management is a key focus, and your doctor will provide strategies to keep you comfortable.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation (2-6 Weeks)
Physical therapy is a crucial part of recovery. During this time, you’ll work with a physical therapist to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in your new hip. Most patients begin walking with assistance soon after surgery and gradually progress to more challenging exercises.
Resuming Normal Activities (3-6 Months)
Within 6 weeks, many patients are able to return to light activities like walking and climbing stairs. However, high-impact activities like running or jumping should be avoided for several months to allow the joint to heal properly.
Full Recovery (6-12 Months)
It can take up to a year for the hip to fully heal and for patients to regain complete strength and flexibility. Regular follow-up visits with your surgeon will help monitor your progress and ensure that the joint is functioning well.
Tips for a Successful Recovery
- Follow Your Doctor’s Instructions: It’s essential to follow the post-surgery instructions carefully to prevent complications and ensure a smooth recovery.
- Stay Active: Engaging in regular physical therapy and gentle exercises will help you regain mobility and strengthen the muscles around your hip.
- Avoid Certain Movements: Your doctor will advise you on specific movements to avoid in the initial months after surgery, such as crossing your legs or bending the hip too far, to prevent dislocation.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet will help support healing and maintain overall health during recovery.
Hip replacement surgery can be a life-changing procedure, offering relief from chronic pain, improved mobility, and the ability to return to daily activities. While the recovery process takes time, the benefits of regaining your quality of life make it a worthwhile option for many people suffering from hip joint issues. If you’re struggling with hip pain and your mobility is being affected, consider discussing hip replacement surgery with your healthcare provider. It could be the key to a pain-free future!
Take control of your health today! If hip pain is affecting your quality of life, talk to your doctor about how hip replacement surgery can help you get back to doing what you love.